The Internet of Things (IoT) is undeniably a game changer in many sectors and industries. An aspect of life where IoT is making significant strides is agriculture. IoT in agriculture is a burgeoning field, promising to revolutionize the way we grow, manage, and consume food. This article will delve into the role of IoT in enhancing agricultural productivity.
The Promise of IoT in Agriculture
The internet of things (IoT) is a network of devices connected to the internet, collecting and sharing data. In agriculture, this technology is used to improve various aspects of farming, including crop health, livestock management, and resource allocation. IoT in agriculture is a way for farmers to leverage technology to increase productivity and efficiency.
Avez-vous vu cela : How Can IoT Improve Air and Water Quality Monitoring in Cities?
Smart Farming
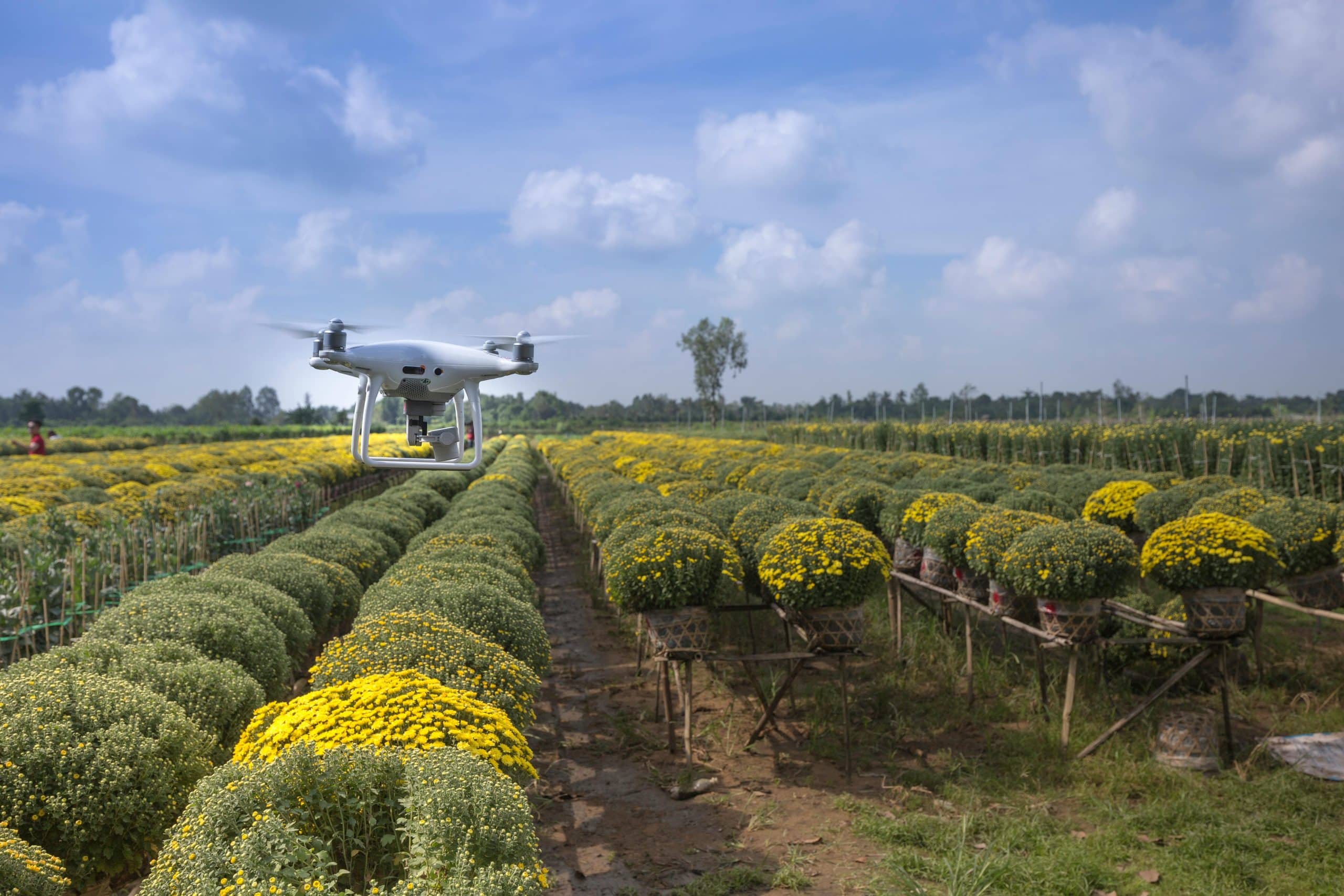
The concept of smart farming is at the heart of IoT in agriculture. By utilizing the latest advancements in technology, farmers can monitor their crops and livestock in real-time, using data collected from sensors, drones, and other IoT devices. This allows them to make more informed decisions about their farming practices, leading to increased productivity and decreased waste.
For instance, a farmer could use sensors to measure soil moisture levels, ensuring that crops receive the right amount of water at the right time. Or, they could use drones to monitor crop health from above, quickly identifying any areas of concern.
Avez-vous vu cela : What Are the Challenges of Integrating IoT in Healthcare Facilities?
Livestock Management
IoT is also playing a pivotal role in livestock management. By attaching IoT devices to animals, farmers can monitor their health and wellbeing in real-time. This knowledge allows them to intervene quickly if an animal becomes sick, preventing the spread of disease and reducing mortality rates.
Additionally, IoT devices can track the location of livestock, reducing the risk of theft or straying. They also collect data on animals’ behavior and movement patterns, which can provide valuable insights into their wellbeing and productivity.
The Impact of IoT on Agricultural Productivity
The impact of IoT on agricultural productivity is significant and multifaceted. By enabling farmers to monitor their operations in real-time, make data-driven decisions, and automate various processes, IoT is helping to increase yields, reduce waste, and improve overall farm efficiency.
Increasing Crop Yields
One of the key ways in which IoT is enhancing agricultural productivity is by increasing crop yields. Through the use of sensors, drones, and other IoT devices, farmers can monitor their crops in real-time, detecting any issues such as disease or pests early. This allows them to take immediate action, preventing crop loss and maximizing yield.
Moreover, IoT devices can help optimize the use of resources like water and fertilizer. For instance, by measuring soil moisture levels, farmers can ensure that their crops receive just the right amount of water, reducing waste and improving crop health.
Reducing Waste and Improving Efficiency
IoT is also helping to reduce waste and improve efficiency in agriculture. By providing farmers with real-time data on their operations, IoT enables them to optimize resource utilization, reduce waste, and increase efficiency.
For instance, a farmer could use IoT devices to track the location and usage of farm equipment, ensuring that it is used efficiently and maintained properly. Similarly, with the help of IoT, farmers can monitor the health and productivity of their livestock, reducing mortality rates and increasing productivity.
The Future of IoT in Agriculture
The future of IoT in agriculture looks promising. As more and more farmers adopt this technology, we can expect to see a significant increase in agricultural productivity.
At the same time, the advent of new and innovative IoT devices and applications will continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in agriculture. From precision farming to smart irrigation systems, the possibilities are endless.
We must also consider the potential challenges and barriers to the widespread adoption of IoT in agriculture. These include issues related to data privacy and security, the need for reliable internet connectivity in rural areas, and the cost of implementing and maintaining IoT systems.
Nevertheless, the benefits of IoT in agriculture far outweigh these challenges. As we move forward, it’s clear that IoT will play an increasingly important role in enhancing agricultural productivity and sustainability.
To sum up, the role of IoT in agriculture is significant and transformative. Its impact on agricultural productivity is already evident and will likely continue to grow in the future. While challenges and barriers to its adoption exist, the potential benefits of IoT in agriculture are immense. As such, IoT represents a promising opportunity to revolutionize agriculture and enhance productivity.
Enhancing Sustainability with IoT in Agriculture
IoT is not just enhancing productivity in agriculture, but also promoting sustainability. The use of IoT devices and applications can help farmers manage their resources more efficiently, minimizing waste and reducing their environmental footprint.
IoT enables precision farming, a method of farming where everything is monitored and managed at a micro level. Precision farming ensures that crops and livestock get exactly what they need, when they need it. This not only boosts agricultural productivity but also significantly reduces waste.
For instance, a farmer can use an IoT device to monitor soil moisture levels, ensuring that crops only get watered when necessary. This not only saves water – a crucial resource in many parts of the world – but also reduces energy waste as less power is needed for irrigation.
Moreover, IoT can help in reducing the use of pesticides by pinpointing exactly where they are needed, which can have a significant positive impact on the local ecosystem, biodiversity, and the health of consumers.
Overcoming Barriers to IoT Adoption in Agriculture
Despite the many benefits of IoT in agriculture, there are challenges that must be addressed for its widespread adoption. These include issues related to data privacy and security, the need for reliable internet connectivity in rural areas, and the cost of implementing and maintaining IoT systems.
Data privacy and security are key concerns in the age of the Internet. Farmers need to be reassured that their data, collected by IoT devices, is kept secure and not misused. This requires robust data protection regulations and secure IoT systems.
Internet connectivity is another challenge. The effectiveness of IoT largely depends on constant and stable internet connectivity. In many rural areas, where most farming activities take place, internet connectivity can be unreliable or even non-existent. Therefore, there is a need for significant investment in rural internet infrastructure to enable the effective use of IoT in agriculture.
Lastly, the cost associated with IoT systems can be a major barrier for many farmers, especially small-scale farmers in developing countries. Hence, it’s important to develop cost-effective IoT solutions and provide financial support to farmers to encourage the adoption of this technology.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things is undoubtedly transforming agriculture, enhancing productivity, and promoting sustainability. It promises a future where farming becomes more efficient, less wasteful, and more environmentally friendly.
Despite the challenges associated with the adoption of IoT in agriculture, the potential benefits are immense. With continued innovation and investment in this area, we can overcome these challenges and realize the full potential of IoT in agriculture.
It’s clear that IoT is not just a buzzword, but a powerful tool that can revolutionize agriculture. As more farmers embrace this technology, we can look forward to a future of increased agricultural productivity, reduced waste, and enhanced sustainability.