In recent years, the concept of smart cities has been a focal point of urban development. A key aspect of making cities smart is enhancing the environment. Monitoring the quality of air and water is pivotal in this regard. The advent of Internet of Things (IoT) has catapulted this monitoring to new levels. This has been made possible by employing IoT based sensors and systems for data collection and analysis. In this engaging read, we aim to dive deep into this subject and explore how IoT can improve air and water quality monitoring in cities.
The Power of IoT in Monitoring Air Quality
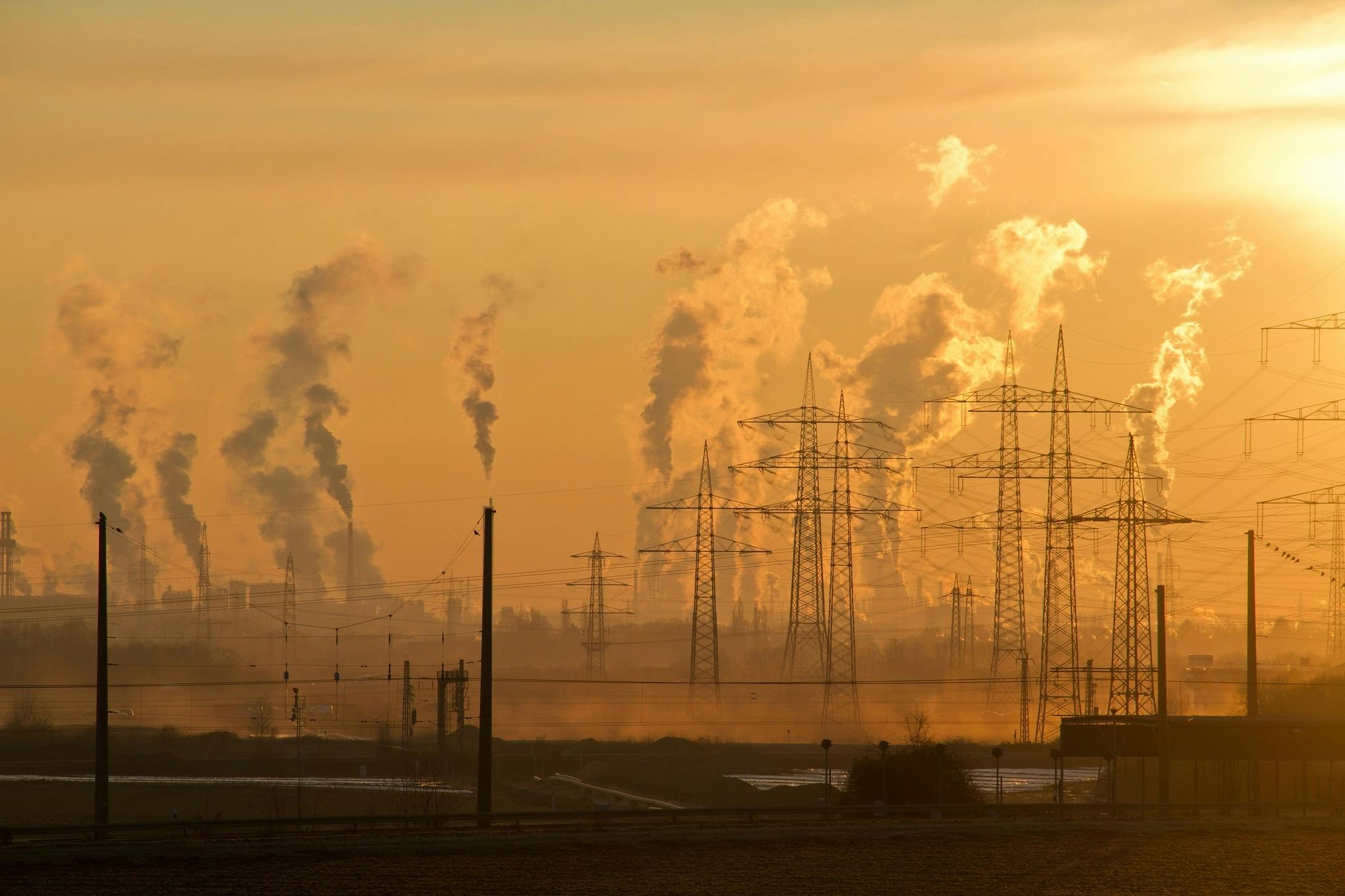
Monitoring air quality in dense urban areas is a pressing need in our times. High levels of pollution can lead to a multitude of health issues for city dwellers. That’s where IoT steps in. Let’s take a closer look at how this revolutionary technology tackles the issue.
Lire également : What Are the Challenges of Integrating IoT in Healthcare Facilities?
IoT offers an efficient and affordable solution to track and monitor air quality. This is achieved through the use of IoT-based sensors. These sensors are small, low-cost devices that can detect and measure various pollutants in the air, such as carbon dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, and particulates.
The gathered data is then transmitted to a cloud server. On this server, sophisticated algorithms and analytics tools assess the data to gauge the air quality in real-time. The output can be readily viewed on digital platforms or mobile applications. This allows for swift actions to be taken in case of harmful pollution levels.
Sujet a lire : What Is the Role of IoT in Enhancing Agricultural Productivity?
Moreover, the IoT-based monitoring system can be integrated with other smart city systems, such as traffic management. This can help to control the source of pollution and ensure better air quality in the city.
In addition, Google has initiated a project wherein Google Street View cars are equipped with air quality sensors. As these cars traverse the city, they collect comprehensive air quality data, which can be used for further analysis and monitoring.
Leveraging IoT for Water Quality Monitoring
Just as with air, monitoring water quality is of utmost importance. Contaminated water can lead to severe health problems and damage the overall ecosystem. IoT can play a significant role in safeguarding water quality. Let’s delve into the specifics of this application.
IoT-based water quality monitoring involves the use of sensors to detect parameters such as pH, temperature, turbidity, and dissolved oxygen in water bodies. These sensors can be attached to buoys or other floating devices and placed in rivers, lakes, or reservoirs. This ensures constant monitoring and instantaneous data collection.
The data collected by these sensors is then transmitted to a cloud server. Like in the case of air quality monitoring, the data is analyzed and interpreted. This allows for immediate identification of any irregularities or instances of pollution.
Furthermore, IoT can be instrumental in detecting leaks and wastage in city water supply systems. This contributes to water conservation and ensures optimal utilization of water resources.
In essence, IoT-based water quality monitoring provides a real-time, accurate, and efficient method of maintaining the health of city water bodies and water supply systems.
The Role of Crossref and Proceedings in IoT Monitoring
Crossref and proceedings play a significant role in the advancement of IoT monitoring systems. Crossref is a scholarly database that contains a wealth of research articles and papers. This resource is invaluable in providing cutting-edge information on the development and application of IoT in quality monitoring.
Researchers and developers can delve into the Crossref database to uncover the latest findings and advancements in IoT technology. This can further enhance the capacity and efficiency of IoT-based monitoring systems.
Similarly, proceedings from conferences and seminars offer a platform for experts to share their insights and experiences in implementing IoT for quality monitoring. These proceedings are often published in scholarly journals or online platforms, making them accessible to the broader IoT community.
In a nutshell, Crossref and proceedings contribute to the continuous evolution and improvement of IoT technology, which in turn, enhances the quality monitoring capabilities.
Various Environmental Systems Based on IoT
In addition to air and water quality monitoring, IoT is used in various other environmental systems. These include waste management, noise pollution monitoring, and weather prediction, to name a few.
For instance, smart waste management systems use IoT sensors to monitor the fill levels of waste bins. This data is then utilized to optimize waste collection routes and schedules, thus improving the efficiency of waste management.
Similarly, IoT sensors can be used to monitor noise pollution levels in different parts of the city. This information can then be used to enforce noise regulations and create quieter, more livable urban spaces.
In terms of weather prediction, IoT devices can collect data on temperature, humidity, wind speed, and other meteorological parameters. This data is then processed and analyzed to predict weather patterns and alert city dwellers of any upcoming adverse weather conditions.
The integration of these various IoT-based environmental systems can result in a comprehensive, smart solution for city management and sustainability.
The Future of IoT-based Quality Monitoring in Cities
Looking ahead, it is clear that IoT will continue to play a pivotal role in improving air and water quality monitoring in cities. The continuous advancements in sensor technology and data analytics will further enhance the accuracy and efficiency of these monitoring systems.
In addition, with the increasing emphasis on sustainable development and smart cities, the integration of IoT-based monitoring systems with other urban infrastructures will become more prevalent. This will lead to more holistic and effective management of urban environments.
Moreover, initiatives such as Google’s air quality project exemplify the potential for collaboration between tech companies, government bodies, and communities. Such collaborations can drive innovative solutions and amplify the impact of IoT in quality monitoring.
In essence, the future of air and water quality monitoring in cities is intertwined with the evolution of IoT technology. Through continuous advancements and innovative applications, IoT is poised to make our cities smarter and healthier.
IoT and Machine Learning: A Powerful Combination for Quality Monitoring
The fusion of IoT and machine learning has the potential to substantially augment the quality monitoring capabilities of smart cities. Machine learning, a subset of artificial intelligence, enables systems to learn from data, identify patterns, and make decisions with minimal human intervention. When combined with IoT, it can significantly enhance the analysis, interpretation, and prediction capabilities of quality monitoring systems.
For instance, in the field of air quality monitoring, machine learning algorithms can process and analyze the raw data collected by IoT sensors. These algorithms can identify patterns in pollution levels and predict future air quality trends. For instance, they may be able to predict spikes in air pollution during certain times of the day or under specific weather conditions.
Similarly, in the realm of water quality monitoring, machine learning can be employed to predict potential instances of water contamination. By analyzing past data, algorithms can identify patterns that may indicate a risk of contamination, such as changes in water temperature or pH levels.
Machine learning can also be instrumental in optimizing the performance of IoT-based monitoring systems. It can analyze the performance data of the sensors and identify any issues or inefficiencies. This can help in maintaining the optimal functioning of the monitoring system and ensuring accurate and reliable data collection.
Moreover, the combination of IoT and machine learning can enable predictive maintenance of urban infrastructures. By analyzing data from IoT sensors, machine learning algorithms can predict potential failures or breakdowns in infrastructures, such as water supply systems or air filtration systems. This can allow for preventive maintenance, thus reducing the risk of failures and ensuring the smooth operation of the city’s infrastructures.
Crossref and Google Scholar: Valuable Resources for IoT Research
Crossref and Google Scholar are invaluable resources for researchers and developers in the field of IoT. Both these platforms house a vast repository of scholarly articles and papers that provide insights into the latest developments in IoT technology and its applications in quality monitoring.
Crossref is a scholarly database that contains research articles and papers from various disciplines, including IoT. Researchers can access Crossref to gain insights into the latest advancements in IoT technology, such as new sensor technologies or data analytics tools.
On the other hand, Google Scholar is a freely accessible web search engine that indexes the full text or metadata of scholarly literature across an array of publishing formats and disciplines. It provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature and allows researchers to keep abreast of the newest innovations in IoT-based quality monitoring.
The articles and papers available on these platforms can provide valuable insights into the practical implementation of IoT in cities. They often include case studies or real-world examples of how IoT has been used to improve air and water quality monitoring. This can serve as a guide for other cities looking to implement similar systems.
To sum up, Crossref and Google Scholar are indispensable tools for researchers and developers in the field of IoT. These platforms provide the latest information and insights, driving the continuous evolution and improvement of IoT technology.
Conclusion
The integration of IoT in air and water quality monitoring has undeniably transformed the landscape of urban environmental management. By providing real-time, accurate data, IoT enables cities to promptly respond to pollution issues and maintain the health of their urban environments.
The fusion of IoT with machine learning can further augment the capabilities of quality monitoring systems. This powerful combination can enable predictive analysis, enhance system performance, and facilitate preventive maintenance of urban infrastructures.
Moreover, resources like Crossref and Google Scholar play a pivotal role in driving the continuous evolution and improvement of IoT technology. They provide researchers and developers with access to the latest information and insights, thereby contributing to the advancement of IoT applications in quality monitoring.
As we look ahead, it’s clear that the future of quality monitoring in cities hinges on the ongoing evolution of IoT technology. By fostering innovation and leveraging collaborations, we can harness the full potential of IoT to make our cities healthier and more sustainable. As we continue to develop and innovate, the dream of truly smart cities becomes ever more attainable.